Identification of Eleutherococcus
According to the requirements of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the medicinal materials are derived from the dried roots and rhizomes or stems of Siberian Ginseng Root.
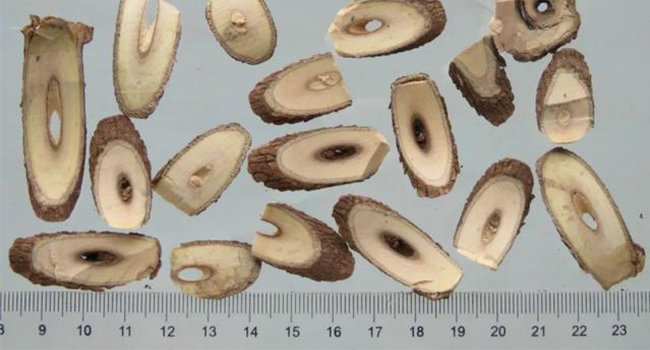
The roots are cylindrical, mostly twisted, 3.5 to 12 cm long, 0.3 to 1.5 cm in diameter; the surface is grayish-brown or dark-brown, rough, with fine longitudinal grooves and wrinkles, thin skin, and some peeling, and the peeling place is gray-yellow. Hard, yellow-white in section, fibrous. It has a peculiar aroma, slightly pungent, slightly bitter, and astringent.


2. Siberian Ginseng rhizome
The rhizome of Eleutherococcus is nodular and irregularly cylindrical, with a diameter of 1.4-4.2cm. The surface is gray-brown or dark-brown, rough, with fine longitudinal grooves and wrinkles, the skin is thin, some peeling off, and the peeling place is grayish-yellow. Hard, yellow-white in section, fibrous. It has a peculiar aroma, slightly pungent, slightly bitter, and astringent.
3. Siberian Ginseng stem
The thorns on the stems of Siberian Ginseng are not static. Eleutherococcus is dense and slightly red on the young stems that have just born in the first year. After the second year, the stems and branches gradually begin to fall off and become brown.
After 2 years, the thorns on the stems fell off cleanly, and the branches became smooth, leaving only round thorn marks. Therefore, it is normal for us to see that eleutherococcus has no thorns.





